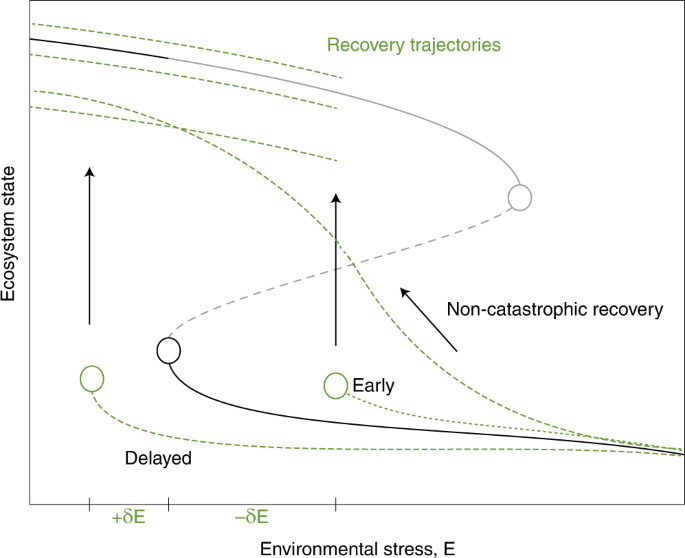
Abstract: "There is growing concern over tipping points arising in ecosystems because of the crossing of environmental thresholds. Tipping points lead to abrupt and possibly irreversible shifts between alternative ecosystem states, potentially incurring high societal costs. Trait variation in populations is central to the biotic feedbacks that maintain alternative ecosystem states, as they govern the responses of populations to environmental change that could stabilize or destabilize ecosystem states. However, we know little about how evolutionary changes in trait distributions over time affect the occurrence of tipping points and even less about how big-scale ecological shifts reciprocally interact with trait dynamics. We argue that interactions between ecological and evolutionary processes should be taken into account in order to understand the balance of feedbacks governing tipping points in nature."
Read More: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41559-019-0797-2